Technology & Products
[Battery Manufacturing] Assembly Process: Finalizing the Structure of Batteries
2025.09.02
|
[Battery Manufacturing] This is a series introducing SAMSUNG SDI’s key battery manufacturing processes. It delivers the core roles and technical characteristics of each of the four processes—electrode, stacking, assembly, and formation—using infographic images. |
Battery manufacturing consists of four process stages: electrode, stacking, assembly, and formation. In the stacking process, the anode and cathode produced during the electrode process are stacked in the sequence of anode–separator–cathode–separator to form a stack.*
* Read more → ①Electrode, ②Stacking Process (Click)

[Cross sections of the electrode and stack]
However, the stack produced in the stacking process does not yet constitute a finished battery. In the case of prismatic batteries, the hexagonal aluminum can casing is finalized in the assembly process.
The assembly process finalizes both the external shape and internal structure of the battery, including inserting the stack into an aluminum can. This step prepares the cell for the subsequent formation process, enabling current to flow within the cell.
The prismatic battery assembly process consists of four main stages: tab welding, can insertion and can-cap welding, electrolyte filling, and sealing and cleaning.

Tap Welding
In the first step, the metal tab from the stack is connected to the cap assembly to enable current flow. The cap assembly is located at the top of the cell and transfers current to the external module while ensuring safety through gas venting and pressure relief.
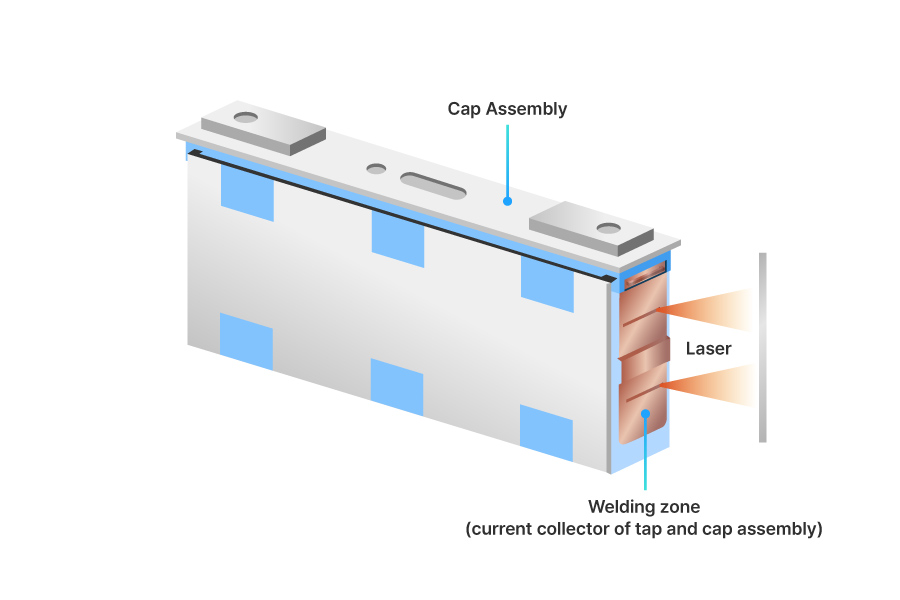
The tabs and cap assembly are joined through welding. Prior to welding, the tabs are precisely aligned to prevent energy loss from the electrode.
The cap assembly is then positioned over the stack, and its current collector is laser-welded to the tabs. Once this step is complete, the stack’s current can be transmitted to the module.
SAMSUNG SDI is minimizing porosity and enhancing welding quality by applying its proprietary patented laser technology, LPW (Laser Plate Welding).
Can Insert & Can-Cap Welding
The second step is inserting the stack into the aluminum can and welding it to complete the external shape of the cell.
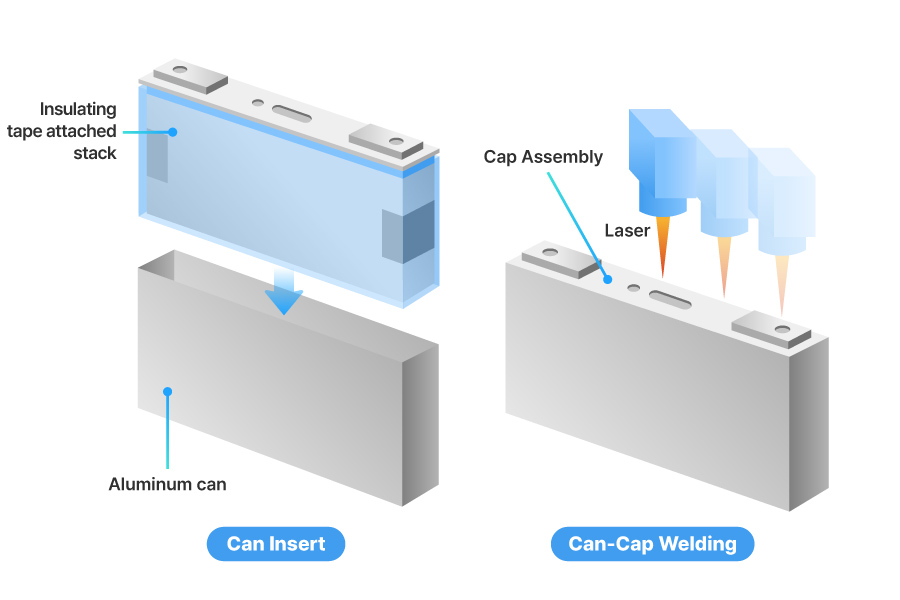
After attaching insulating tape to five sides of the stack (excluding the top), the stack is placed inside the aluminum can, and the cap assembly is pressed in from the top. The insulating tape prevents short circuits that could occur if the electrodes directly touch the can during insertion, which could ensure both quality and safety.
Once the insertion is complete, the can and cap assembly are laser-welded to completely seal any gaps. This prevents outside air from entering or the electrolyte from leaking.
EL Filling
The third step is injecting electrolyte into the cell. The electrolyte is a liquid that enables lithium ions to move inside the battery.
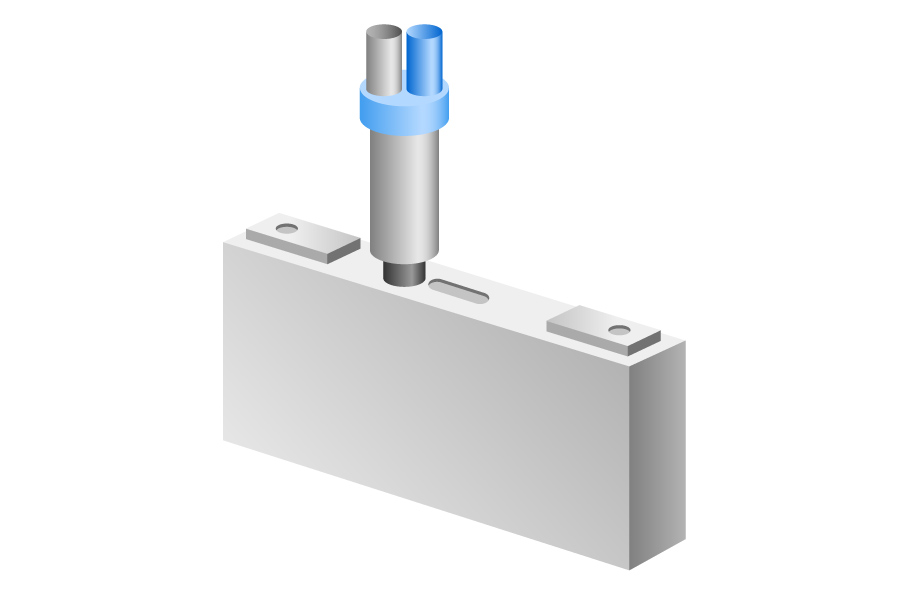
Before injection, the cell is tested under vacuum to see if there are any small leaks. If no issues are found, a predetermined amount of electrolyte is injected.
The cell then undergoes an “impregnation” process, during which the electrolyte fully and evenly penetrates the electrodes and ensures stable ion transport.
Sealing & Cleaning
The last step is sealing the cell and cleaning the external case.
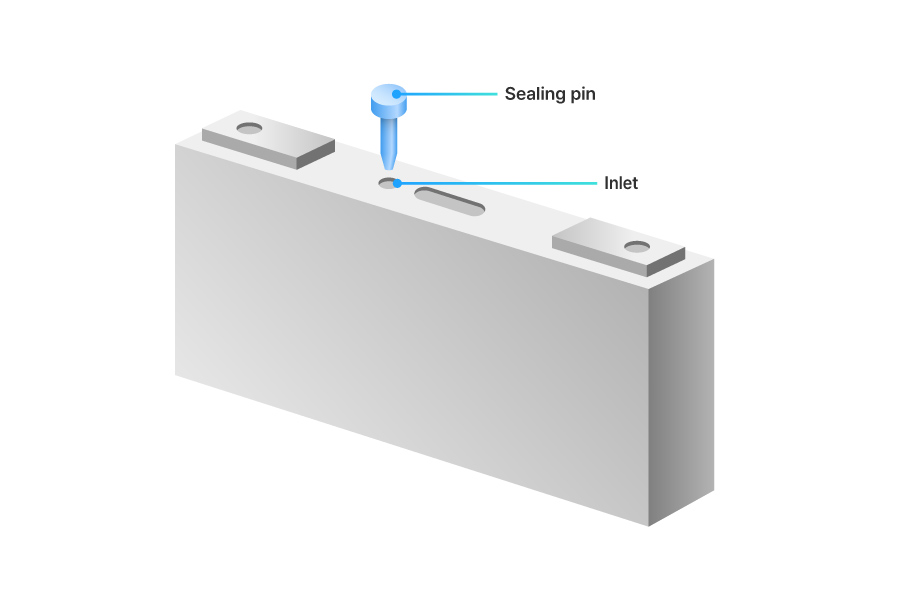
After thoroughly cleaning the electrolyte inlet, we temporarily seal it to prevent leakage. Then we perform internal resistance and pressure tests to confirm proper current flow and sealing integrity.
After inspection, the cell is washed with water on the top surface and dried using a suction device to clean its exterior. The cell is then examined for contamination or damage before proceeding to the next stage, the formation process which initiates current flow.
