Technology & Products
[Battery Glossary] Charging, Discharging, Fast Charging, CC/CV
2025.05.29
|
[Battery Glossary] answers the questions related to batteries with key term explanation. From fundamental battery principles, manufacturing processes to emerging next-generation technologies, [Battery Glossary] makes battery concepts easy to understand. |
Charging
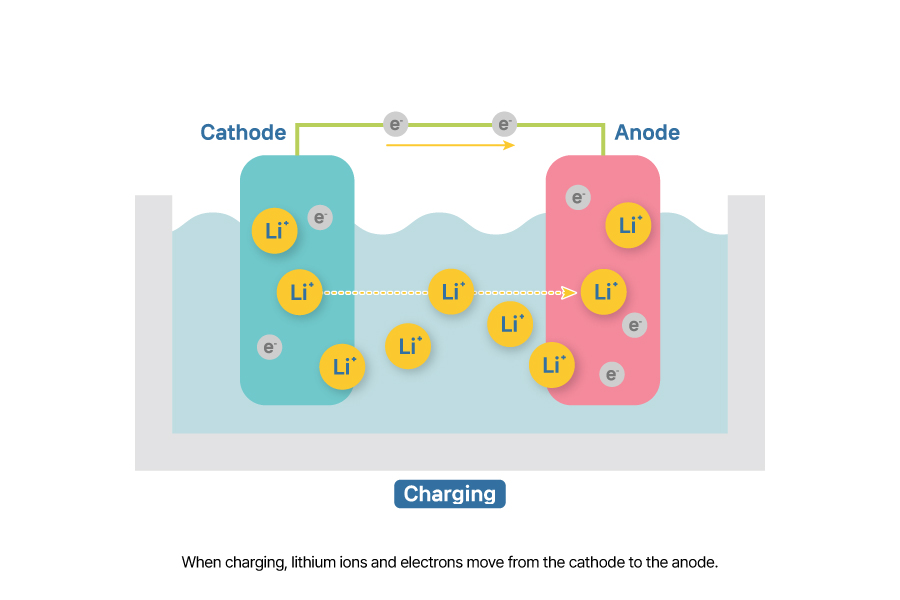
Charging is the process of storing lithium ions and electrons in the anode by reversing a chemical reaction using external energy. When voltage is applied during charging, lithium ions and electrons move from the cathode to the anode. Lithium ions travel through the electrolyte, while electrons move through an external circuit to reach and be stored in the anode.
Transfers of electrons in a battery can be explained through oxidation and reduction reactions. Losing electrons is called oxidation reaction, while gaining electrons is called reduction. During charging, oxidation occurs at the cathode because it loses electrons, and reduction occurs at the anode because it gains electrons.
Discharging
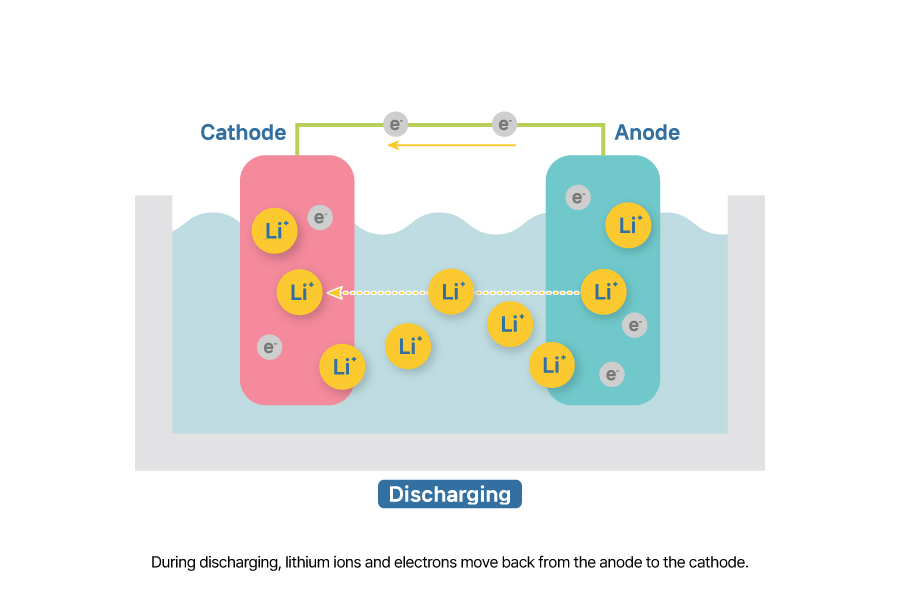
Discharging is the process of converting the chemical energy stored in the battery into electrical energy. Discharging is a spontaneous reaction, during which the lithium ions and electrons stored in the anode during charging are released back to the cathode. Similar to charging, lithium ions move through the electrolyte and electrons move through an external circuit to the cathode. The transfer of electrons generates a current, which can be used to power devices.
Transfers of electrons in a battery can be explained through oxidation and reduction reactions. Losing electrons is called oxidation reaction, while gaining electrons is called reduction. During discharging, reduction occurs at the cathode because it gains electron, and oxidation occurs at the anode because it loses electrons.
Fast Charging
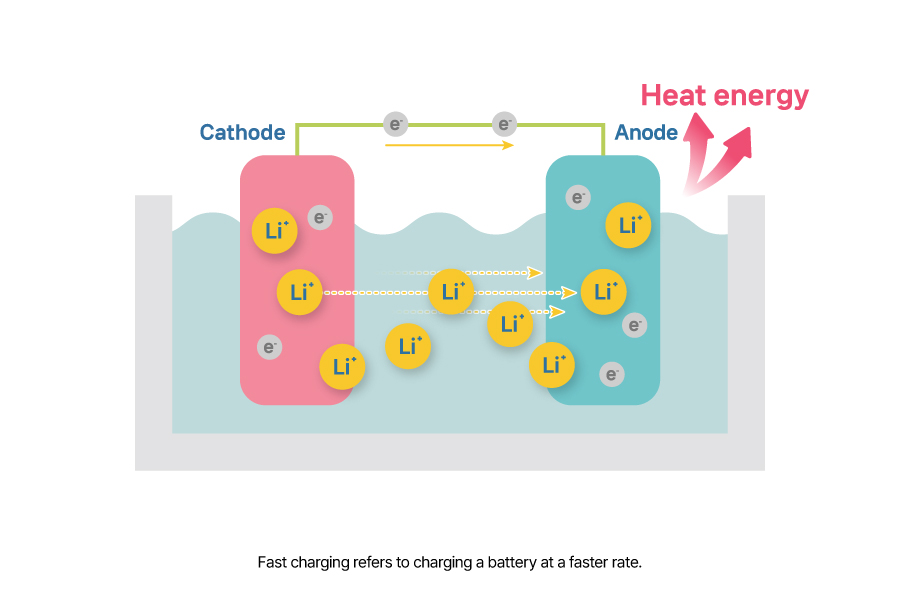
Fast Charging literally refers to charging a battery at a faster rate within a given period. This method increases the speed of charging by using chargers with higher current or voltage. The battery’s internal structure must be designed to handle the discharging process.
Fast charging typically generates more heat than regular charging. During charging and discharging, some of the energy from the chemical reactions is converted to heat. In fast charging, the reaction processes are accelerated, leading to higher heat generation. Overheating is a significant cause of battery performance degradation. To address this, SAMSUGN SDI is developing efficient charging technologies.
CC/CV
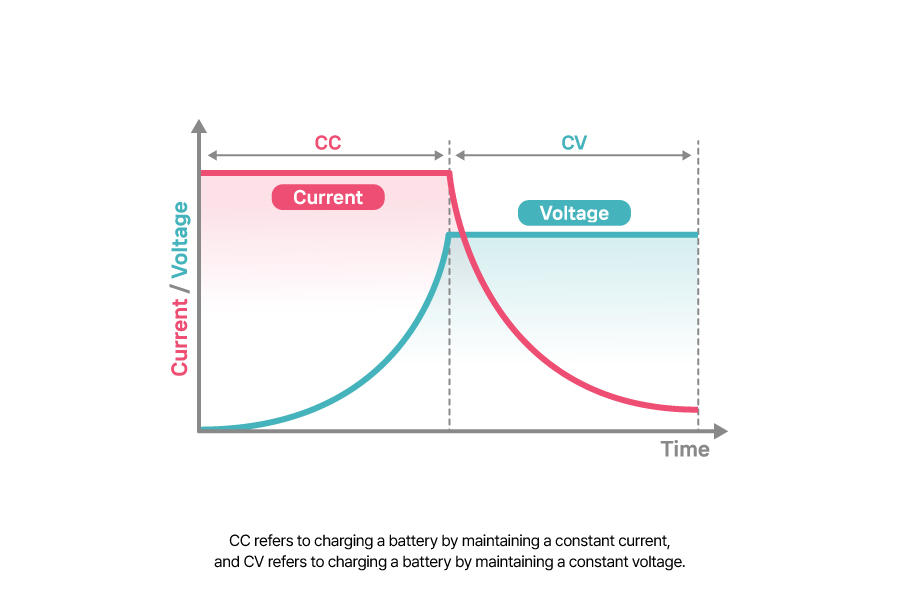
CC and CV are conditions used in the process of charging and discharging a battery. Let me explain the process based on the charging scenario. CC (Constant Current) refers to charging a battery by maintaining a constant current. It is designed to supply a constant current until the battery reaches the limit cell voltage, ensuring a consistent flow of lithium ions and electrons.
CV (Constant Voltage) refers to charging a battery by maintaining a constant voltage. Under the CV condition, the current can vary. Generally, CV is a method used during the final stage of charging to supply constant current until the battery is fully charged. Therefore, using the CC method in the initial stage of charging and then switching to CV in later stages will charge a battery with 100% of the battery capacity.
This process can be compared to filling a cup with water. Pouring a fixed amount of water to fill the cup is akin to CC charging. However, due to factors like splashing, the cup may not be completely full. To ensure the cup is 100% full, CV is like adjusting the flow and carefully topping it off.
