Technology & Products
[Battery Glossary] Power, Capacity, Energy Density, Resistance, EV/HEV/PHEV
2025.04.15
|
[Battery Glossary] answers the questions related to batteries with key term explanation. From fundamental battery principles, manufacturing processes to emerging next-generation technologies, [Battery Glossary] makes battery concepts easy to understand. |
Power 
Power refers to the amount of electric energy a battery generates per one second. It is expressed in watt (W) and is calculated by multiplying the voltage (V) and the current (A). High-output batteries can deliver greater power per unit of time. However, high-output batteries are not always better because their powerful performance can accelerate physical degradation of the battery. Therefore, high-output batteries may not be suitable for devices requiring long lifespan.
Capacity
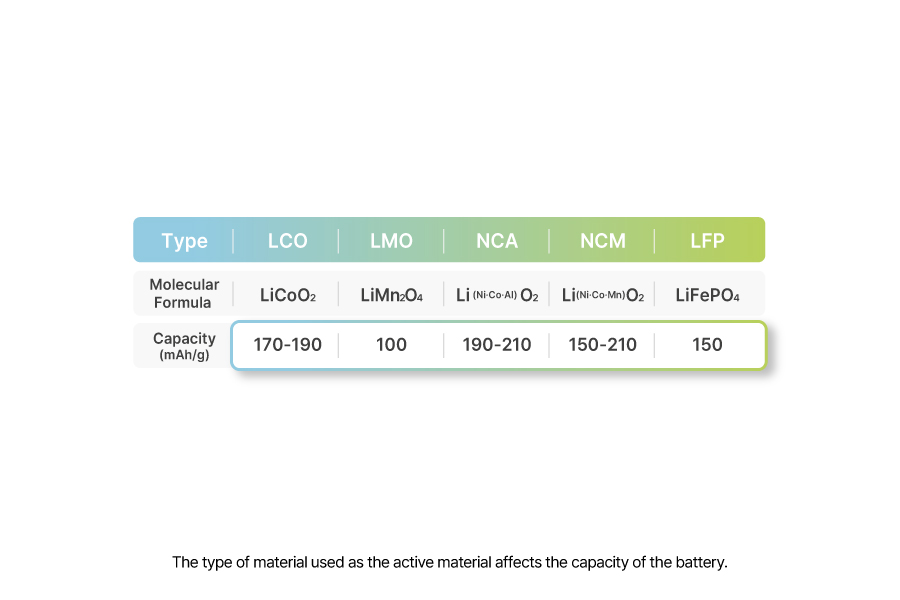
Capacity refers to the total amount of electricity a battery can store. It indicates how much electricity can be discharged, or used, over a certain period. Capacity is calculated by multiplying current (A) and time (h), and its unit is ampere-hours (Ah).
One of the key factors determining battery capacity is the cathode active material. The type of material used as the active material affects the capacity of the battery. Additionally, the more cathode active material used, the greater the battery capacity. For example, in lithium-ion batteries, materials like NCM or NCM are used as cathode active materials, with lithium added. Lithium plays a vital role in energy generation by moving between the anode and cathode in ionic form. Therefore, cathode active materials containing lithium are crucial in determining a battery’s capacity.
Energy Density
Energy in a battery refers to ‘the total stored electrical energy’. It is calculated by multiplying voltage (V), current (A), and time (h), and its unit is a watt-hour (Wh).
Energy Density refers to the amount of stored electrical energy per unit volume or weight. It indicates how much electrical energy can be stored in a limited space or weight. Energy density is calculated by dividing the total electrical energy by either volume or weight and is expressed in Wh/L or Wh/kg.
A battery with high energy density can store the same amount of electrical energy in a similar volume or lighter weight. For example, applying high-energy-density batteries to electric vehicles allows for more efficient use of space inside the vehicle.
Resistance
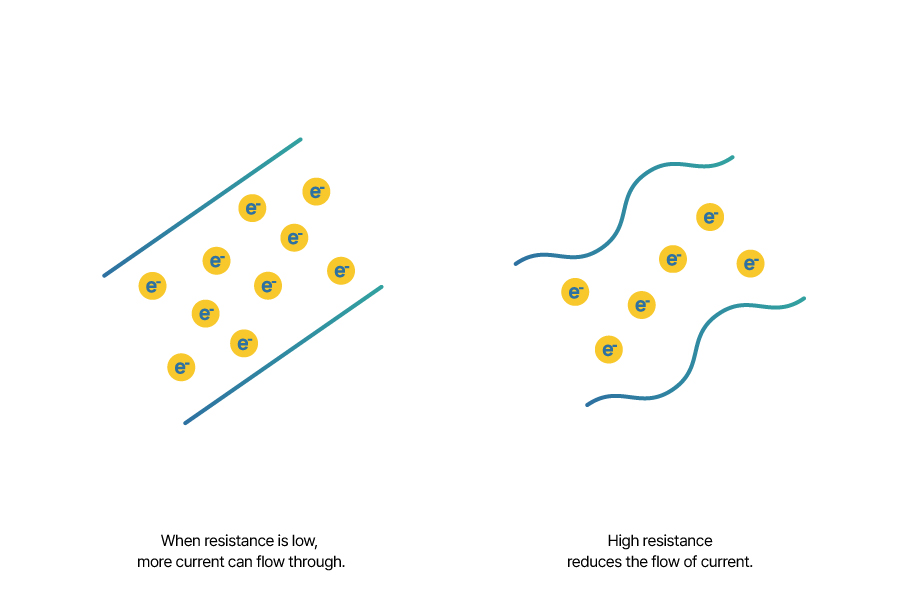
Resistance refers to the opposition to the flow of electric current. To put it simply, it indicates how well a battery can allow current to pass through its internal structure. Resistance can also be used to control the strength of the current. When resistance is low, more current can flow through, whereas high resistance reduces the flow of current.
The higher the resistance, the more chemical energy inside the battery is converted into heat energy instead of electrical energy, leading to a loss of electrical energy. Therefore, batteries with low resistance generally exhibit better performance, as they experience less power loss compared to high-resistance batteries.
EV/PHEV/HEV
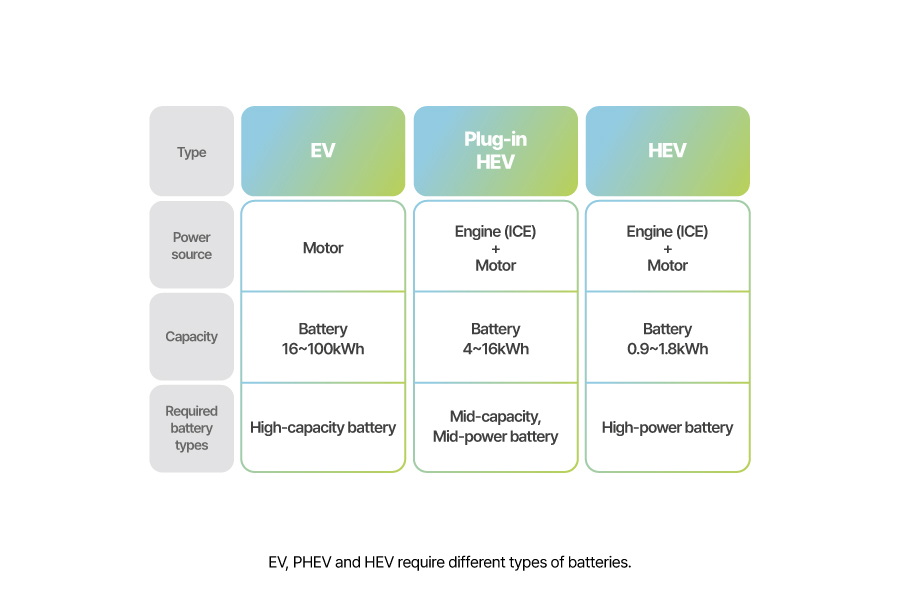
EV (Electric Vehicle) relies solely on electric motor for propulsion, with no engine involved. This reduces the number of components, resulting in a simpler structure with no noise or vibration. EVs typically require 100-500 cells with high energy density and large capacity.
PHEV (Plug-in HEV) primarily uses an electric motor as the main power source, while the engine serves as an auxiliary power source. They can be charged externally via a power outlet. Typically, PHEVs use 100-300 cells. Since electricity is the primary energy source, the required cell capacity is relatively larger compared to HEVs.
HEV(Hybrid Electric Vehicle) is a conventional internal combustion engine vehicle with the addition of an electric motor and a low-capacity battery. The electric motor and engine work together for tasks requiring high power or high-spend driving. For lower power demands, such as starting the vehicle or low-speed driving, the electric motor is used. Since the electric motor is an auxiliary power source in HEVs, they typically require 30-100 cells with similar capacity requirements.
