Technology & Products
[Battery101] Type of EV Batteries
2024.09.06
|
101[wʌ́nouwʌ́n] means basic knowledge of a topic or collection of introductory materials to a topic. Our Battery 101 series talks about all things battery: the history, technical aspects (basic principles and mechanisms), industrial aspects (IT, electric vehicles, ESS, etc.), and next-generation technologies that SAMSUNG SDI will innovate while opening up its future. Batteries have infinite potentials that exceeds our wildest imagination. Through Batteries 101 series, you will have a chance to see the entire spectrum of the battery's possibilities and to conjure SAMSUNG SDI’s pivotal role in it. |
Start of Three Kingdoms: cylindrical, prismatic, pouch
When you think of EVs batteries, you might imagine a large rectangular frame laid out across the bottom of the vehicle. However, if you take a closer look inside, each vehicle is equipped with different types of batteries, such as prismatic, pouch, and cylindrical.
Prismatic cells are the most common EV battery type among them, but they are not the dominant No. 1 in terms of installation rates. A fair amount of pouch and cylindrical type batteries are used as well. It is as if we are in the period of Three Kingdoms, where three different types of batteries are in fierce competition. Then why do we use different types of cells for different cars instead of one unified-type cell? Let’s find out reasons why and the characteristics of each battery type.
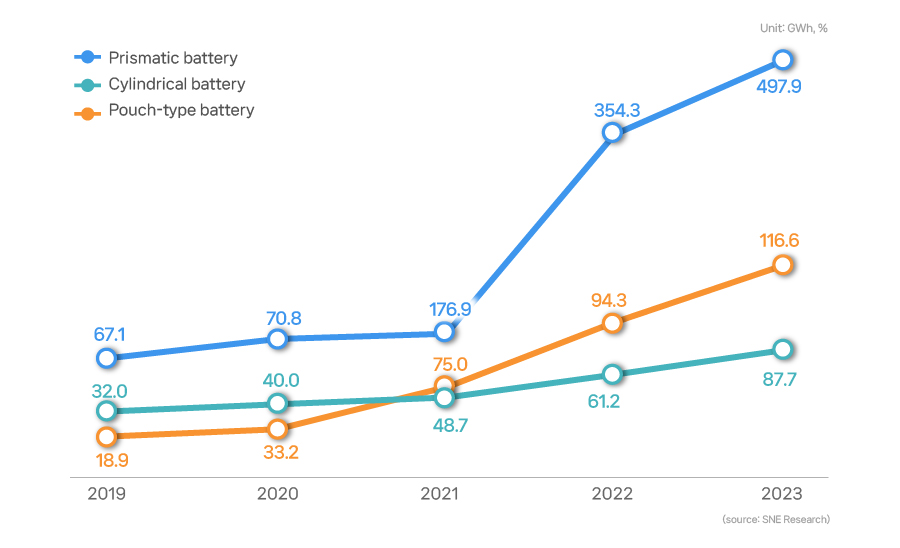
[EV battery installation trend for each battery type]
Cylindrical batteries can be used for EVs
Until the mid-2000s, almost no one would have thought of a cylindrical battery being used for EVs. Although they have high energy density despite their small size, cylindrical batteries are often used in power tools or vacuum cleaners that require instant high output. However, they fall short of capacity to be installed in an EV because thousands of them are needed for an EV. Then, what’s the reason for the current use of cylindrical batteries in EVs?

[SAMSUNG SDI’s cylindrical battery]
First, technological maturity. Cylindrical batteries are safe and reliable when it comes to manufacturing method as they have been around for a long time with technological advancements. Especially for EVs, the development already requires countless number of technologies, so verified technologies are also being widely adopted for EV battery, which helped the adoption of cylindrical batteries in this context.
Second, price competitiveness through mass production: Mass production literally means producing as many products per hour as possible. For this, safe manufacturing method should ensue along with fast manufacturing process to increase the yield rate. Cylindrical batteries can be manufactured quickly by winding materials into a jelly roll, which is a very distinct advantage compared to pouch-type and prismatic cells.
Prismatic cells are the dominant player in the market
Prismatic batteries that are dominant among EV batteries have a similar structure with aluminum can case. The battery contents are placed in a rigid aluminum can sealed with a lid, and then completely sealed using laser welding. Just as canned food rarely goes bad for decades after production, prismatic batteries also have a long lifespan and are resistant to external shocks.
Batteries generate heat during charging and discharging. More heat is generated when delivering high performance, such as fast charging or high power output. If the heat is not dissipated properly, the heat accumulated in the battery can degrade performance, shorten battery life, causing safety risks such as swelling due to internal damages. This is where the advantages of prismatic cells come into play, as aluminum has a high thermal conductivity to dissipate heat, acting as a cooler. Because cells with high external shock resistance and excellent cooling capability have a stronger price competitiveness as the manufacturing process of modules or packs can be streamlined.

[SAMSUNG SDI's EV Battery Cell]
Pouch cells are encased in thin casing, which is quite a contrast to their cylindrical and prismatic counterparts. Because pouch cells are designed with soft, reflective, and thin film, they are relatively lightweight, come in a variety of sizes, and have a higher energy density. Pouch cells are more susceptible to external impact than cylindrical and prismatic batteries, so it requires technology to compensate for this when assembling into modules or packs, and the production cost is also higher.
