Technology & Products
[Battery Manufacturing] Stacking Process: Stacking Cathode, Anode and Separator
2025.08.05
|
[Battery Manufacturing] This is a series introducing SAMSUNG SDI’s key battery manufacturing processes. It delivers the core roles and technical characteristics of each of the four processes—electrode, stacking, assembly, and formation—using infographic images. |
The stacking process involves stacking the anode, cathode, and separator before placing them into the can. Samsung SDI applies this process to its prismatic batteries. It allows for more efficient use of space inside the can, thereby increasing the energy density, and since there are no bent areas in the electrodes or separator, it also offers advantages in terms of safety.
The stacking process consists of four main stages: notching and cutting, inspection, stacking, and post processing.
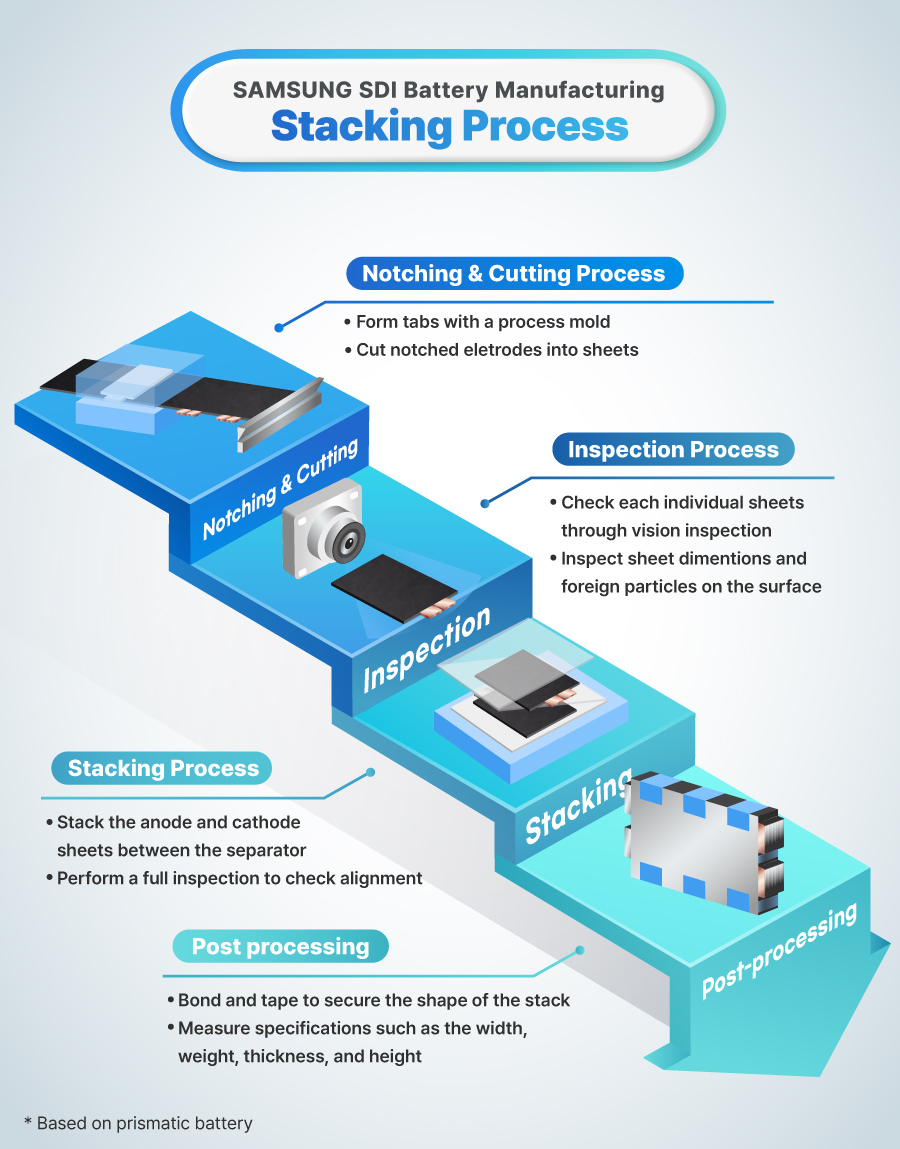
Nothing & Cutting Process
The notching and cutting process involves forming tabs on the anode and cathode and then cutting them into sheets.
*Tab: A pathway that allows current from the electrode substrate to flow.
The anode and cathode are then transported in the form of reels*—rolled up like toilet paper. These reels are fed into the equipment, where they are unrolled for further processing.
*Reel: A winding device used to store slit electrode and transfer them to the next process.
When the unrolled electrode passes through a press mold, tabs are formed. This is known as the notching process. The press mold, shaped like a tab, works like a cookie cutter to form tabs. Thanks to this, the stacking process has the advantage of not being limited to a specific form factor. By simply changing the size of a press mold, it can flexibly accommodate various sheet sizes. The notched electrodes are then cut into individual sheets by a cutter. This step is called the cutting process.
Inspection Process
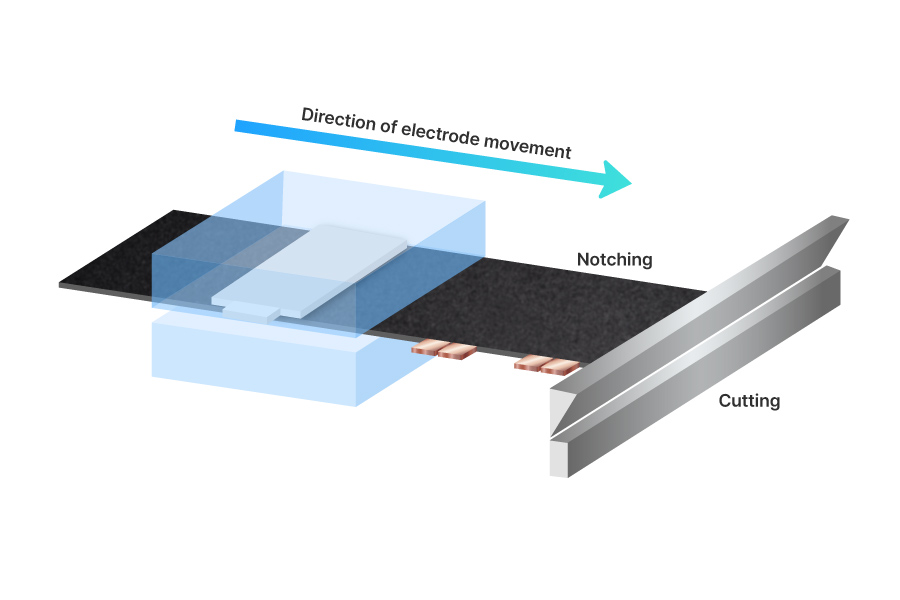
The inspection process is carried out before stacking begins. Each individual sheet is checked through a vision inspection system.
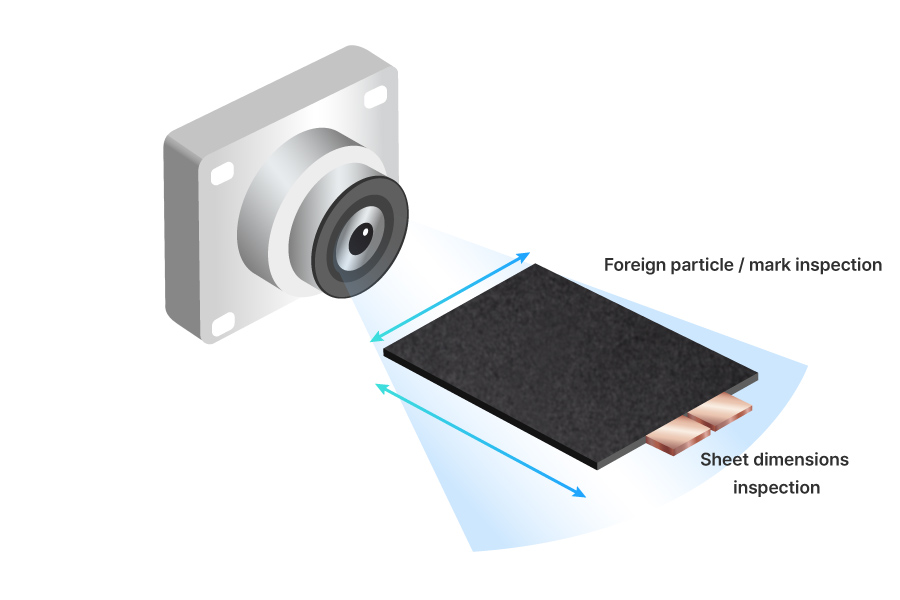
In this process, the dimensions of each sheet are inspected, and any marks or foreign particles on the surface are checked. Uniform sheet size and the absence of defects or contaminants are essential to ensure the sheets are neatly aligned during stacking. This process checks sheet dimensions and defects such as marks or foreign particles. Uniform sheet size and the absence of defects or contaminants are essential to ensure the sheets are aligned during stacking.
After the inspection process, sheets are transported by robot to the next stage, where the anode and cathode sheets are positioned on either side of the stack table. The stack table is where the next process takes place, serving as the main stage for full-scale stacking.
Stacking Process
The stacking process involves layering the anode and cathode with separators in between. Sheets are stacked in the order of anode-separator-cathode to form a stack.
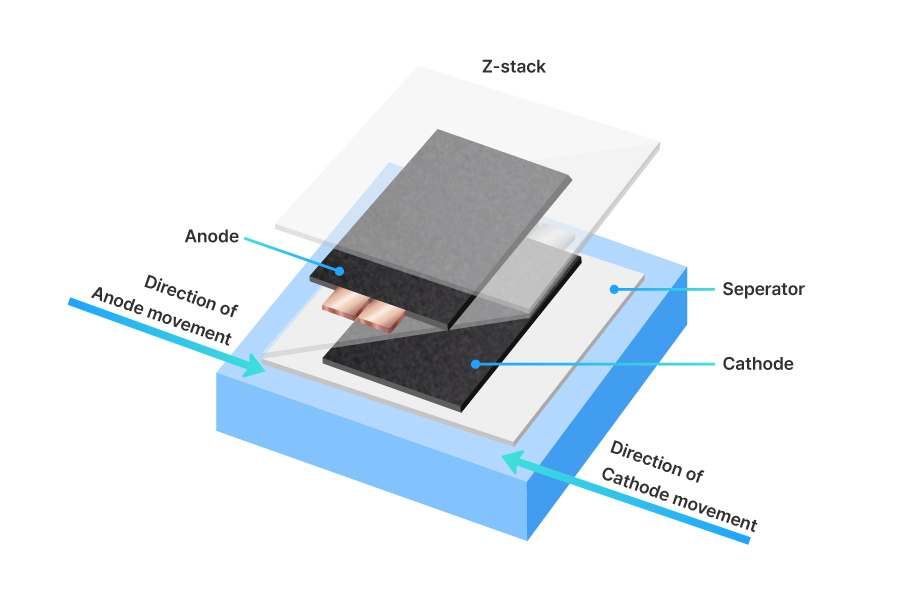
The detailed process is as follows. First, the separator is lowered onto the stack table, and the anode is placed on top of it. Another separator is then placed, held in place from the side, and followed by the cathode. This method of alternately layering sheets with separators folded in a ‘Z’ shape is called ‘Z-stacking’.
To ensure precise and safe stack production, SAMSUNG SDI performs a full inspection of all sheets after stacking is complete. Specifically, a vision inspection is conducted to check whether the electrode and separators are properly aligned and whether there are any protrusions.
Post Processing
The post processing consists of bonding and taping to secure the shape of the stack, followed by a measurement step to assess the stack’s physical specifications.
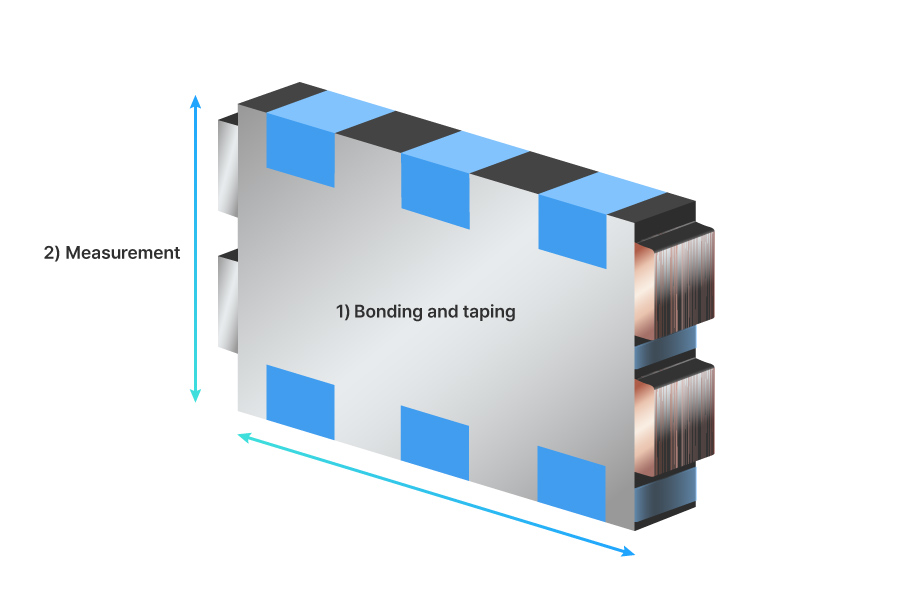
The purpose of the bonding and taping is to ensure that the stacked anode, cathode, and separators remain firmly fixed during subsequent processes or transportation. First, adhesive is applied between the tabs for primary bonding, and then tape is applied along the sides of the stack. The final stage measures key specifications such as the stack’s width, weight, thickness, and height.
