Technology & Products
[Battery Manufacturing] Electrode Process: Manufacturing Key Components of a Battery
2025.07.22
|
[Battery Manufacturing] This is a series introducing SAMSUNG SDI’s key battery manufacturing processes. It delivers the core roles and technical characteristics of each of the four processes—electrode, stacking, assembly, and formation—using infographic images. |
The electrode process of SAMSUNG SDI is a procedure to make the anode and cathode, which are key components of a battery. It consists of four main stages: mixing, coating, slitting, and pressing. Each of these steps plays a critical role in determining the performance and quality of the battery.
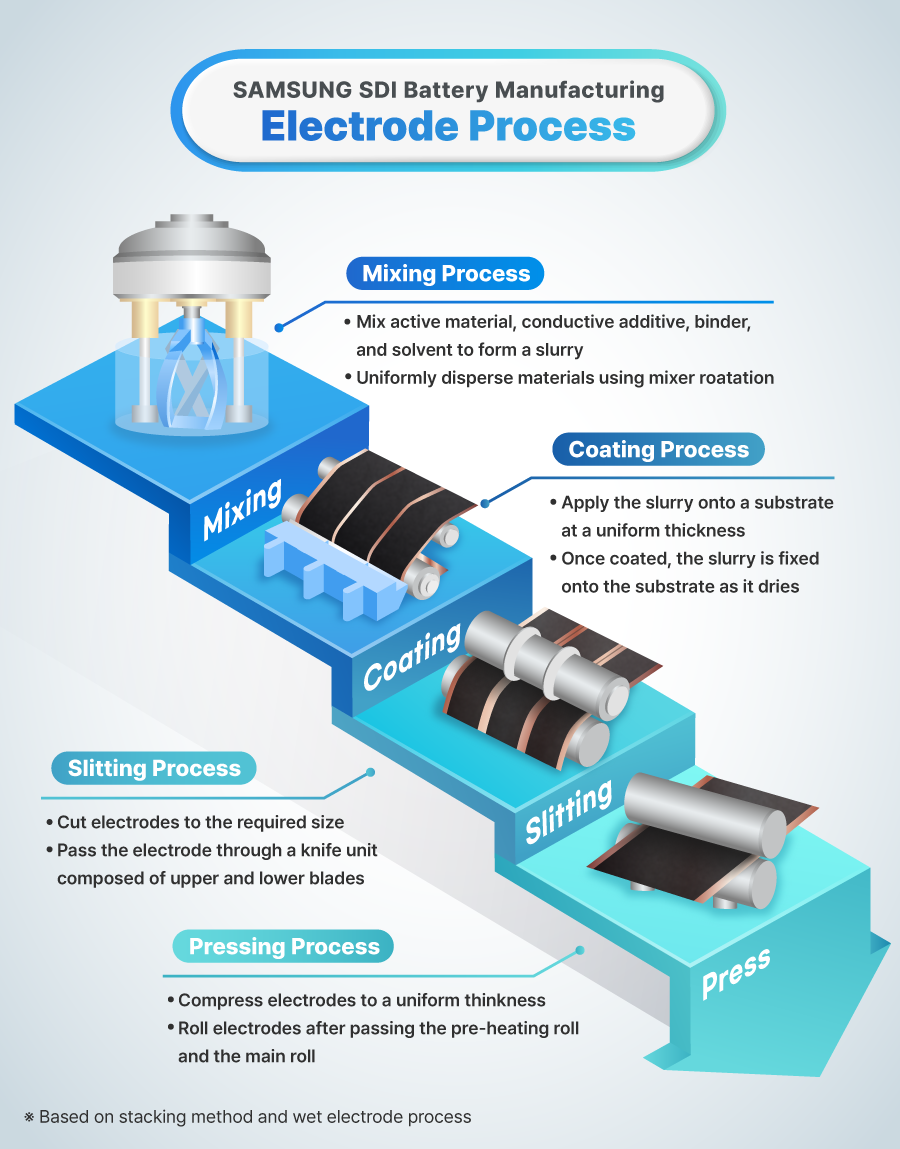
Mixing Process
The mixing process produces a slurry by mixing the key battery materials such as active material, conductive additive, binder, and solvent in specific ratios.
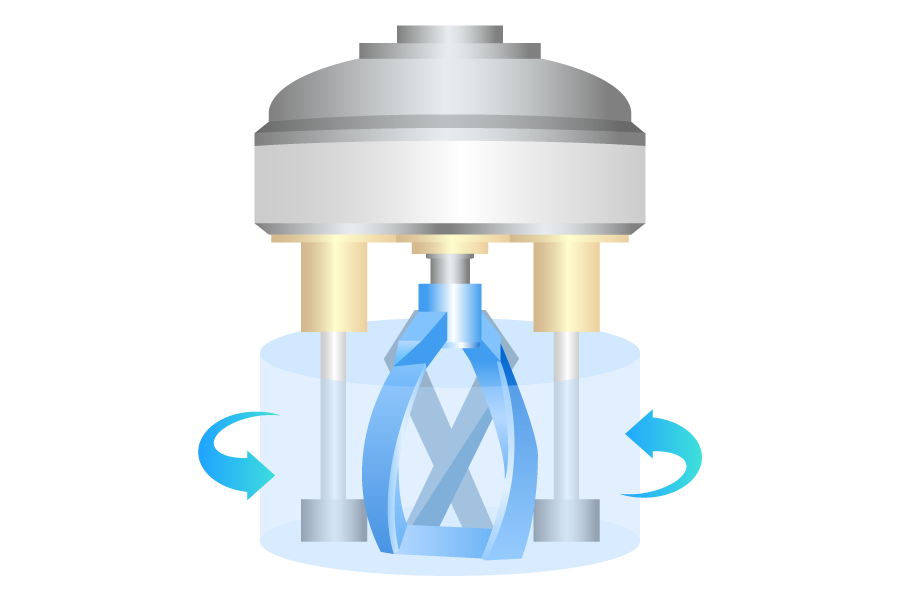
Each mixed material is uniformly dispersed using the rotational force of the mixer. Subsequently, metal foreign substances and air bubbles are removed to ensure quality and safety.
Once the slurry is prepared, it is stored for a certain period in a coating buffer tank, where it is mixed with previously prepared slurry. This process improves the uniformity of the slurry quality and ensures a stable supply rate for the subsequent coating process.
Coating Process
The coating process applies the slurry produced in the mixing process onto a metal substrate (current collector) at a uniform thickness and then dries it. Aluminum is used as the substrate for the cathode, while copper is used for the anode.
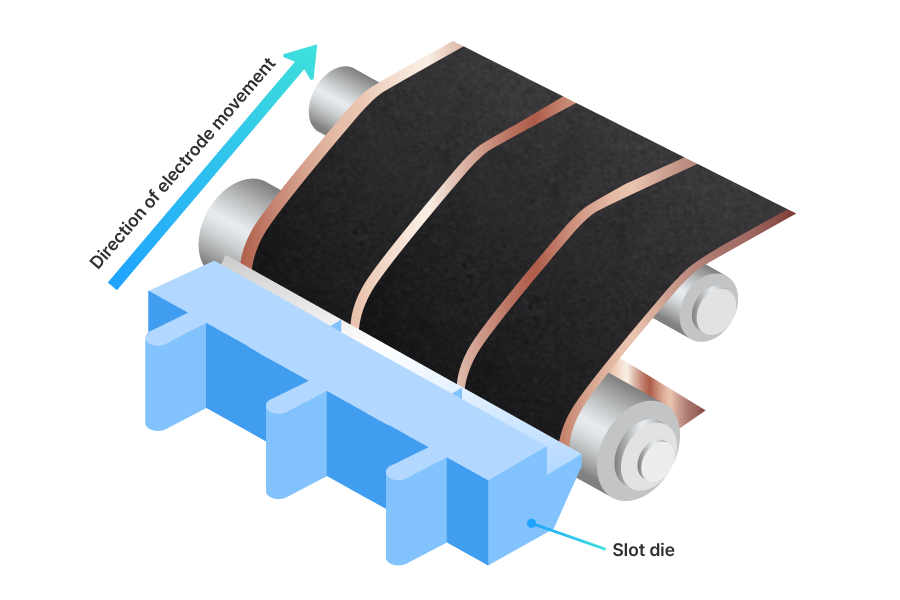
The slurry is applied using a "slot die", a precision coating device that dispenses the slurry through a single outlet. The slot die controls the width and position of the coating as the substrate continuously moves through the process. SAMSUNG SDI uses a technology that allows individual control of the width and position even during multi-line coating.
Additionally, it enhances electrode and battery performance by adjusting the direction of graphite particles within the electrode and varying the material composition between the upper and lower layers of the electrode.
Once the slurry is coated, it undergoes a drying process in which the solvent evaporates, allowing the material to be stably fixed onto the surface of the substrate.
Slitting Process
The slitting process cut the coated electrode into specified widths and winds them onto reels*. This prepares the electrode for the subsequent stacking or winding processes.
* Reel: A winding device used to store slit electrode and transfer them to the next process.
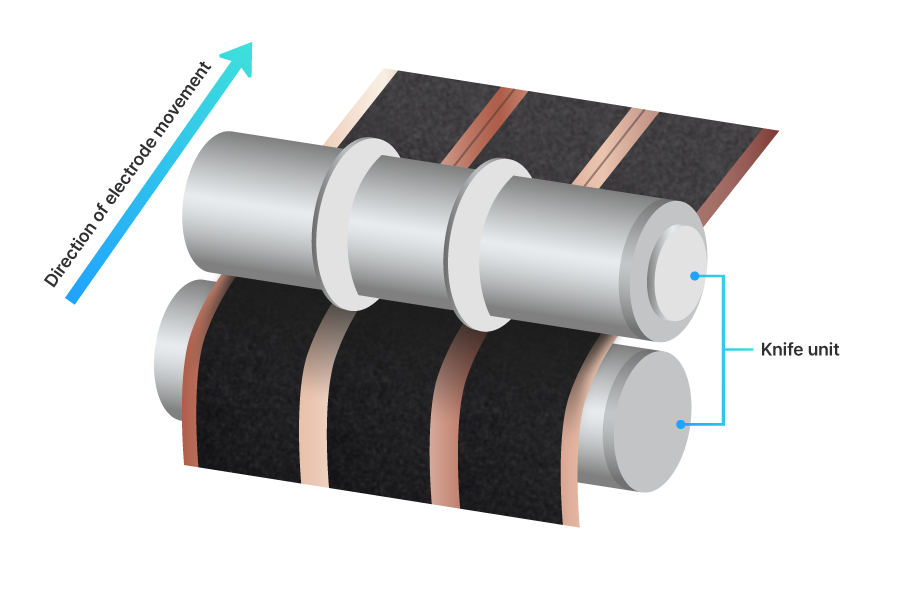
The electrode is precisely cut by the knife unit*, which is the core component of the slitter machine.
After the electrode is cut, foreign substances on the surface are removed and wound onto multiple reels. A key factor in this stage is tension control. If the tension is too high or too low, defects such as improper winding or wrinkling may occur.
To prevent such issues, the slitter is equipped with a real-time tension control system that ensures the electrode is wound evenly onto the reels.
* Knife Unit: Composed of an upper blade and a lower blade. The angle and overlap between the blades directly affect the cutting quality.
Pressing Process
The pressing process compresses the slit electrodes to a specified thickness, thereby increasing capacity density and enhancing adhesion between the active material and substrate.
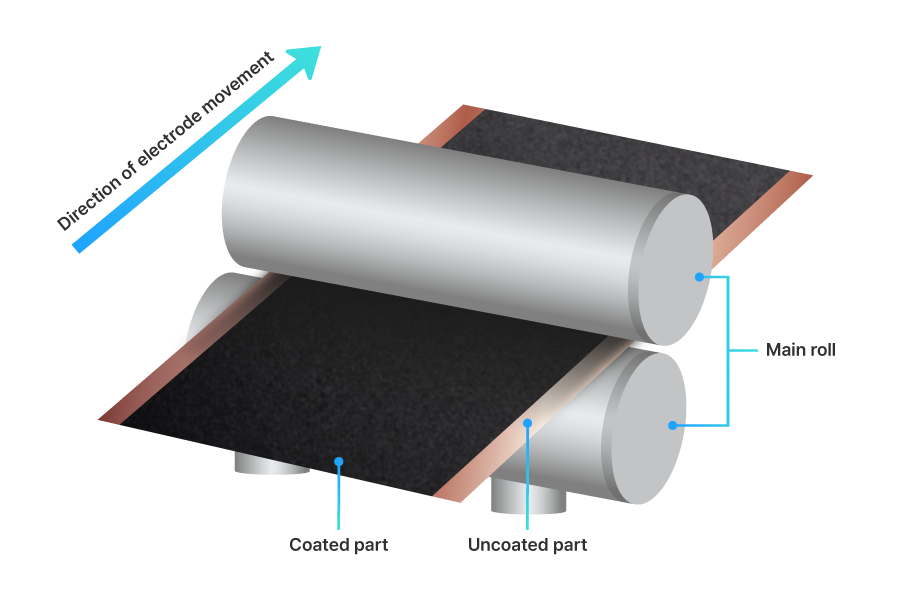
The electrodes first pass through a pre-heating roll to raise their internal temperature to a certain level, and are then compressed to the target thickness as they pass through the main roll.
In the case of cathode electrodes, the coated part with active material stretches during the rolling process, whereas the uncoated part without active material does not. To prevent damage to the substrate caused by this tension differences, SAMSUNG SDI is currently applying a new process to control it.
|
Dry Electrode Recently, dry electrode technology, which takes a different approach from conventional wet electrode process, has also gained traction. This technology compresses the electrode active material into a solid power and forms it into a thin film, which is then attached to the substrate. By eliminating steps such as solvent use and drying, the technology streamlines the production process and enhances productivity through reduced energy consumption. |
In September 2024, SAMSUNG SDI completed constructions of the ‘DryEV Line’, a pilot line for the dry electrode process and continues to develop related technologies. Going forward, SAMSUNG SDI will continue to advance its electrode process technologies.
